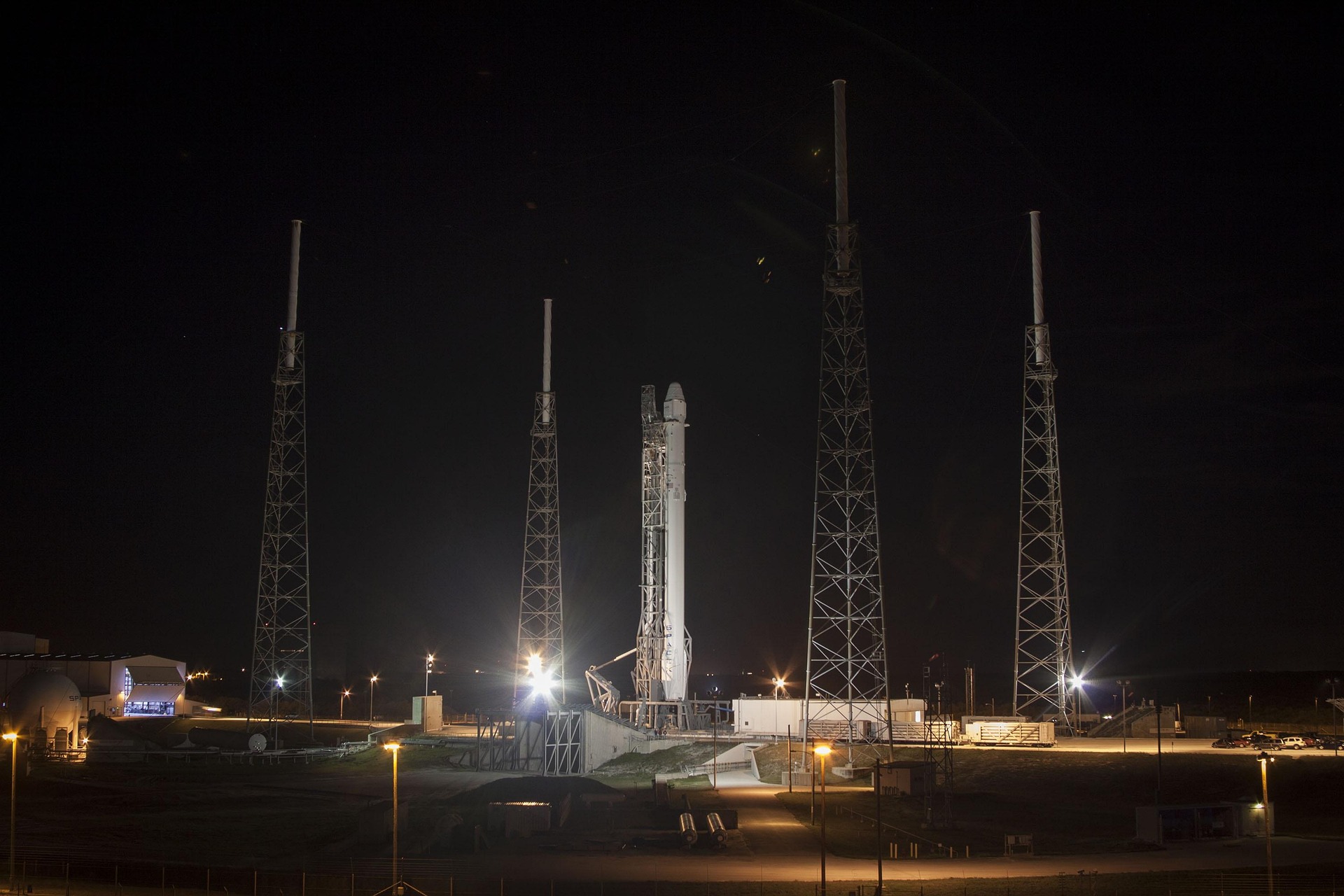
On April 1, 2025, SpaceX achieved a groundbreaking milestone with its Fram2 mission, becoming the first-ever crewed spaceflight to enter a polar retrograde orbit. This historic journey marked a significant leap in human space exploration, setting the stage for new possibilities in space research, Earth observation, and interplanetary missions. The mission’s success is not just a triumph for SpaceX but a defining moment in the future of space travel, expanding the horizons of what’s possible for both science and human presence beyond Earth.
The significance of a polar retrograde orbit
A polar orbit occurs when a spacecraft passes over Earth’s poles, allowing for complete global coverage as the planet rotates beneath it. This type of orbit is crucial for environmental monitoring, weather forecasting, and global communications due to its ability to provide consistent views of the entire surface of the Earth. What makes the retrograde aspect of the Fram2 mission even more remarkable is that the spacecraft’s trajectory was opposite to Earth’s rotation, providing a more challenging flight path and opening doors to more efficient orbit planning for future missions.
The retrograde orbit enables enhanced satellite imaging capabilities and more stable observation for scientific purposes, which has immense applications in climate research, military reconnaissance, and global data collection. Prior to Fram2, achieving a retrograde orbit required a heavier expenditure of energy and fuel. However, SpaceX’s technological advancements have made it more feasible and energy-efficient to send crewed missions into these orbits, demonstrating the company’s ability to push the boundaries of spaceflight.
SpaceX’s technological achievement and impact on future missions
This mission builds on SpaceX’s impressive legacy of reusable rocket technology, following the successful deployment of the Falcon Heavy and Starship programs. For Fram2, SpaceX used the Starship spacecraft to launch the crew and its payload into orbit, marking the first time this spacecraft was used for a crewed mission beyond low Earth orbit (LEO). With its powerful engines and the ability to carry large payloads, Starship’s role in achieving this mission’s success demonstrates the versatility and capability of SpaceX’s next-generation spacecraft.
By completing the journey into a polar retrograde orbit, SpaceX has not only set a precedent for future human spaceflights but also paved the way for interplanetary missions. The company is now positioned to play a significant role in the upcoming Artemis missions, NASA’s ambitious goal to return humans to the Moon, and beyond, to Mars. Polar orbits could be crucial for missions to other celestial bodies, as they provide a more efficient way to monitor regions of planets and moons that are difficult to observe from standard orbits.
Scientific and research potential unlocked
The Fram2 mission opens new research opportunities that could revolutionize space science. As the spacecraft flew over the poles, its sensors collected invaluable data on Earth’s magnetosphere, atmospheric conditions, and space weather phenomena. The mission also carried a variety of scientific instruments designed to monitor cosmic radiation, offering new insights into the impact of space travel on human health.
Additionally, the Fram2 mission featured a unique experiment to test long-duration life support systems for future deep-space exploration. The crew, who spent nearly a week aboard the spacecraft, participated in tests that simulated the conditions they would face on extended missions to the Moon or Mars. These tests will help refine life support systems and habitat technology, ensuring that astronauts can survive in the harsh environments of space for extended periods.
Global partnerships and future implications
The success of SpaceX’s Fram2 mission is not just a win for the private sector but a leap forward for international cooperation in space exploration. In addition to SpaceX’s own resources, the mission involved collaboration with NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), among others, showcasing the growing trend of global partnerships in space. These partnerships will be essential for the ambitious goals set for future space exploration, particularly for missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
What’s next for SpaceX and crewed spaceflights?
SpaceX’s polar retrograde orbit achievement is just the beginning. With Starship’s ongoing development and advancements in reusable rocket technology, the company is well on its way to expanding human space travel capabilities even further. The Fram2 mission not only positions SpaceX as a leader in crewed space exploration but also sets the stage for more ambitious missions that will pave the way for humanity’s long-term presence in space.
In the coming years, we can expect to see more polar missions, along with deep-space flights that will test the limits of human exploration and knowledge. SpaceX’s unwavering focus on innovation, sustainability, and efficiency ensures that the future of space exploration is full of exciting possibilities, and the Fram2 mission is a pivotal step in making those possibilities a reality.
As the world reflects on the success of SpaceX’s historic journey, it’s clear that space exploration is entering an exciting new chapter—one defined by bold ventures, international collaboration, and an ever-expanding horizon of human potential beyond Earth.